Difference between revisions of "Kilroy Danger Signal"
(Created page with '[[File:ARTS1913FigurePage103.jpg|thumb|400px|'''Kilroy's Danger Signal wiring'''<br>As seen in the ''Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1913''<ref>''Annual Report of the Torped…') |
(use Citable Source Templates in place of longhand <ref>s) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:ARTS1913FigurePage103.jpg|thumb|400px|'''Kilroy's Danger Signal wiring'''<br>As seen in the ''Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1913'' | + | [[File:ARTS1913FigurePage103.jpg|thumb|400px|'''Kilroy's Danger Signal wiring'''<br>As seen in the ''Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1913''{{ARTS1913|p. 103}} ]] |
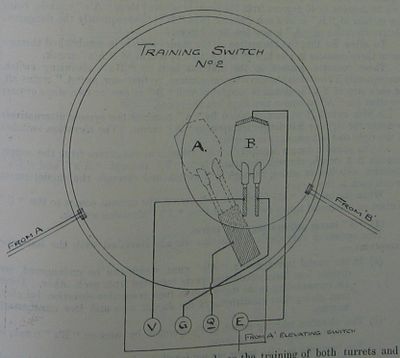
'''Kilroy's Danger Signal''' was an automated system to detect and signal when the blast from one turret's guns might endanger the guns of another turret based on their present training and elevation angles. | '''Kilroy's Danger Signal''' was an automated system to detect and signal when the blast from one turret's guns might endanger the guns of another turret based on their present training and elevation angles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate73.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate74.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate75.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate76.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate77.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate78.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate79.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate80.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate81.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate82.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate83.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate84.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate85.jpg| | ||
| + | File:HandbookFCInstruments1914Plate86.jpg| | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
It was one of several contributions of [[Willie Dickson Kilroy]], an inventor and officer in the [[Royal Navy Volunteer Reserve]]. | It was one of several contributions of [[Willie Dickson Kilroy]], an inventor and officer in the [[Royal Navy Volunteer Reserve]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When the system detected an unsafe firing condition, a loud audible alarm from a warning trumpet would sound in the endangering turret, and it was to be taken to mean, "Don't fire!" A visual indication would accompany the sound. | ||
| + | {{HFCI1914|p. 53}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | It was widely deployed until the ''Iron Duke'' class inaugurated Kilroy's more assertive [[Danger Zone Fire Control]] system which locked the firing triggers when trouble was likely.<ref>''Handbook for Fire Control Instruments, 1914, p. 59.</ref> The successor technology was probably used thereafter.{{INF}} | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Danger Zone Fire Control]] |
| − | + | ||
==Footnotes== | ==Footnotes== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 34: | ||
==Bibliography== | ==Bibliography== | ||
{{refbegin}} | {{refbegin}} | ||
| − | * | + | *{{HFCI1914}} |
{{refend}} | {{refend}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Fire Control]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Shipboard Equipment]] |
Latest revision as of 16:14, 26 September 2012
Kilroy's Danger Signal was an automated system to detect and signal when the blast from one turret's guns might endanger the guns of another turret based on their present training and elevation angles.
It was one of several contributions of Willie Dickson Kilroy, an inventor and officer in the Royal Navy Volunteer Reserve.
When the system detected an unsafe firing condition, a loud audible alarm from a warning trumpet would sound in the endangering turret, and it was to be taken to mean, "Don't fire!" A visual indication would accompany the sound. [2]
It was widely deployed until the Iron Duke class inaugurated Kilroy's more assertive Danger Zone Fire Control system which locked the firing triggers when trouble was likely.[3] The successor technology was probably used thereafter.[Inference]
See Also
Footnotes
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1913. p. 103.
- ↑ Handbook for Fire Control Instruments, 1914. p. 53.
- ↑ Handbook for Fire Control Instruments, 1914, p. 59.
Bibliography
- Admiralty, Gunnery Branch (1914). Handbook for Fire Control Instruments, 1914. G. 01627/14. C.B. 1030. Copy 1235 at The National Archives. ADM 186/191.