Acorn Class Destroyer (1910): Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
Simon Harley (talk | contribs) (Added costs.) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" border=2 cellpadding=2 cellspacing=0 style="margin: 0 0 1em 0.5em; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px #aaa solid; border-collapse: collapse;" align=center; | {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" border=2 cellpadding=2 cellspacing=0 style="margin: 0 0 1em 0.5em; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px #aaa solid; border-collapse: collapse;" align=center; | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan= | ! colspan=7 align=left|Overview of 20 vessels | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan= | | colspan=7 align=left|<small>Citations for this data available on individual ship pages unless otherwise stated</small> | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align=center | Name | ! align=center | Name | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
! align=center | Completed | ! align=center | Completed | ||
! align=center | Fate | ! align=center | Fate | ||
! align=center | Cost<ref>''Navy (Dockyard Expense Accounts), 1912–1913''. p. 143.</ref> | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Acorn | | {{Template:UK-Acorn}} | ||
|[[John Brown]] | |[[John Brown & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|1 Jul, 1910 | |1 Jul, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| Nov, 1921 | | Nov, 1921 | ||
| £98,373 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Alarm | | {{Template:UK-Alarm}} | ||
|[[John Brown]] | |[[John Brown & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|29 Aug, 1910 | |29 Aug, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| May, 1921 | | May, 1921 | ||
| £95,212 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Brisk | | {{Template:UK-Brisk}} | ||
|[[John Brown]] | |[[John Brown & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|20 Sep, 1910 | |20 Sep, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| Nov, 1921 | | Nov, 1921 | ||
| £102,310 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Sheldrake | | {{Template:UK-Sheldrake}} | ||
|[[Denny]] | |[[William Denny & Brothers]] | ||
| | | | ||
|18 Jan, 1911 | |18 Jan, 1911 | ||
| | | | ||
| Nov, 1921 | | Nov, 1921 | ||
| £95,881 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Staunch | | {{Template:UK-Staunch}} | ||
|[[Denny]] | |[[William Denny & Brothers]] | ||
| | | | ||
|29 Oct, 1910 | |29 Oct, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
|Torpedoed 11 Nov, 1917 | |Torpedoed 11 Nov, 1917 | ||
| £93,053 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Cameleon | | {{Template:UK-Cameleon}} | ||
|[[Fairfield]] | |[[Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|1 Jun, 1910 | |1 Jun, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| Nov, 1921 | | Nov, 1921 | ||
| £98,671 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK- | | {{Template:UK-1Comet}} | ||
|[[Fairfield]] | |[[Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|23 Jun, 1910 | |23 Jun, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
|Torpedoed 6 Aug, 1918 | |Torpedoed 6 Aug, 1918 | ||
| £95,581 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Goldfinch | | {{Template:UK-Goldfinch}} | ||
|[[Fairfield]] | |[[Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|12 Jul, 1910 | |12 Jul, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
|Wrecked 19 Feb, 1915 | |Wrecked 19 Feb, 1915 | ||
| £94,758 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Nemesis | | {{Template:UK-Nemesis}} | ||
|[[Hawthorn Leslie]] | |[[Hawthorn Leslie & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|9 Aug, 1910 | |9 Aug, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
|To Japan Jun, 1917 | |To Japan Jun, 1917 | ||
| £97,752 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Nereide | | {{Template:UK-Nereide}} | ||
|[[Hawthorn Leslie]] | |[[Hawthorn Leslie & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|6 Sep, 1910 | |6 Sep, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| Dec, 1921 | | Dec, 1921 | ||
| £95,673 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Nymphe | | {{Template:UK-Nymphe}} | ||
|[[Hawthorn Leslie]] | |[[Hawthorn Leslie & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|31 Jan, 1911 | |31 Jan, 1911 | ||
| | | | ||
| May, 1921 | | May, 1921 | ||
| £94,895 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK- | | {{Template:UK-1Fury}} | ||
|[[Inglis]] | |[[A. & J. Inglis]] | ||
| | | | ||
|25 Apr, 1911 | |25 Apr, 1911 | ||
| | | | ||
| Nov, 1921 | | Nov, 1921 | ||
| £95,793 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Hope | | {{Template:UK-Hope}} | ||
|[[Swan Hunter]] | |[[Swan Hunter]] | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 111: | Line 124: | ||
| | | | ||
| Feb, 1920 | | Feb, 1920 | ||
| £94,574 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Larne | | {{Template:UK-Larne}} | ||
|[[Thornycroft]] | |[[John I. Thornycroft & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|23 Aug, 1910 | |23 Aug, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| May, 1921 | | May, 1921 | ||
| £89,838 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Lyra | | {{Template:UK-Lyra}} | ||
|[[Thornycroft]] | |[[John I. Thornycroft & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|4 Oct, 1910 | |4 Oct, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| May, 1921 | | May, 1921 | ||
| £86,267 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Martin | | {{Template:UK-Martin}} | ||
|[[Thornycroft]] | |[[John I. Thornycroft & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|15 Dec, 1910 | |15 Dec, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| Aug, 1920 | | Aug, 1920 | ||
| £85,243 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Minstrel | | {{Template:UK-Minstrel}} | ||
|[[Thornycroft]] | |[[John I. Thornycroft & Company]] | ||
| | | | ||
|2 Feb, 1911 | |2 Feb, 1911 | ||
| | | | ||
|To Japan Jun, 1917 | |To Japan Jun, 1917 | ||
| £85,141 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Redpole | | {{Template:UK-Redpole}} | ||
|[[J. | |[[J. Samuel White]] | ||
| | | | ||
|24 Jun, 1910 | |24 Jun, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| May, 1921 | | May, 1921 | ||
| £97,081 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Rifleman | | {{Template:UK-Rifleman}} | ||
|[[J. | |[[J. Samuel White]] | ||
| | | | ||
|22 Aug, 1910 | |22 Aug, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| May, 1921 | | May, 1921 | ||
| £94,866 | |||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| {{UK-Ruby | | {{Template:UK-Ruby}} | ||
|[[J. | |[[J. Samuel White]] | ||
| | | | ||
|4 Nov, 1910 | |4 Nov, 1910 | ||
| | | | ||
| May, 1921 | | May, 1921 | ||
| £94,617 | |||
|} | |} | ||
</div name=fredbot:ships> | </div name=fredbot:ships> | ||
==Fittings== | |||
{{UK-Minstrel}} and {{UK-Nereide}} had experimental water-excluding ventilators, and were asked to report on their effectiveness just as the war was about to start.{{AWO1914|184 of 24 July, 1914}} | |||
In October 1914, as the ''Acorns'' were all serving in the {{UK-DF|2}}, they were ordered to have the (hydraulic?) searchlight control system first used in {{UK-Badger|f=p}} fitted.{{AWO1914|454 of 6 Oct, 1914}} | |||
==Performance== | ==Performance== | ||
They burned oil, unlike the [[Beagle Class Destroyer (1909)|''Beagle''s]], delivering the same 27 knots on a displacement 200 tons lighter. | Six of the ships were found to have developed leaks caused by vibration at high speed running: {{UK-Acorn}}, {{UK-Alarm}}, {{UK-Larne}}, {{UK-Lyra}}, {{UK-Nymphe}} and {{UK-Rifleman}}.<ref>"Good Firing On The China Station." ''The Times'' (London, England), Saturday, Jul 08, 1911; pg. 15; Issue 39632.</ref> | ||
They burned oil, unlike the [[Beagle Class Destroyer (1909)|''Beagle''s]], delivering the same 27 knots on a displacement 200 tons lighter.{{UKTHVol4Part34|p. 11}} | |||
While the individual ships certainly varied widely, they were described as having a radius of 2250 NM at 13 knots.{{March|p. 109}} | While the individual ships certainly varied widely, they were described as having a radius of 2250 NM at 13 knots.{{March|p. 109}} | ||
''Acorn'' achieved 4 miles to the ton of coal at 27.5 knots. {{UK-Redpole}} topped out at a spry 30.61 knots in rough weather! | ''Acorn'' achieved 4 miles to the ton of coal at 27.5 knots. {{UK-Redpole}} topped out at a spry 30.61 knots in rough weather!{{March|p. 113}} | ||
''Comet'' had the smallest tactical diameter (402 yards starboard, 536 port, advance of 354 yards), and {{UK-Redpole}} had the worst diameters at 728 yards to starboard and 608 to port. The ships burned around 7 tons per hour at full speed and 0.75 tons per hour at cruising speed.{{March|p. 113}} | ''Comet'' had the smallest tactical diameter (402 yards starboard, 536 port, advance of 354 yards), and {{UK-Redpole}} had the worst diameters at 728 yards to starboard and 608 to port. The ships burned around 7 tons per hour at full speed and 0.75 tons per hour at cruising speed.{{March|p. 113}} | ||
| Line 176: | Line 206: | ||
==Armament== | ==Armament== | ||
The gun armament used here was similar to that of the preceding [[Beagle Class Destroyer (1909)|''Beagle'' class]], although the 12-pdrs were no longer mounted in echelon. A similar scheme would carry forward into the [[Acheron Class Destroyer (1910)|''Acheron'' class]] with minor variations in mountings and positioning of the 12-pdrs. | The gun armament used here was similar to that of the preceding [[Beagle Class Destroyer (1909)|''Beagle'' class]], although the 12-pdrs were no longer mounted in echelon. A similar scheme would carry forward into the [[Acheron Class Destroyer (1910)|''Acheron'' class]] with minor variations in mountings and positioning of the 12-pdrs. | ||
In late September, 1914, the Admiralty ordered that the guns on the [[Tribal Class Destroyer (1907)|Tribals]] and later classes were to be given loading lights, initially on temporary circuits.{{AWO1914|416 of 29 Sep, 1914}} | |||
===4-in Guns=== | ===4-in Guns=== | ||
The two 4-in guns mounted fore and aft were 4-in B.L. Mark VIII on P III mountings with 120 rounds per gun.{{March|p. 109}} | The two 4-in guns mounted fore and aft were 4-in B.L. Mark VIII on P. III mountings with 120 rounds per gun.{{March|p. 109}}{{TheSightM|pp. 4, 88, 108, Plate 42}} | ||
The mounting could elevate to 20 degrees and depress to 10 degrees, but though its sight could match the 20 degree elevation, the range dial was only graduated to 9,300 yards (14 degrees 44 arc minutes) at 2,225 fps. | The mounting could elevate to 20 degrees and depress to 10 degrees, but though its sight could match the 20 degree elevation, the range dial was only graduated to 9,300 yards (14 degrees 44 arc minutes) at 2,225 fps. | ||
The gear-worked sight had a range gearing contant of 54 and spiral-reading range dials were provided for 2225 fps, 1-in aiming rifle and .303-in aiming rifle. | The gear-worked sight had a range gearing contant of 54 and spiral-reading range dials were provided for 2225 fps, 1-in aiming rifle and .303-in aiming rifle. M.V. could be corrected by adjustable pointer to +/- 75 fps. | ||
The deflection gearing constant was 50.69 with 1 knot equal to 3.05 arc minutes, corresponding to 2275 fps at 2000 yards. Drift was corrected by inclining the sight 2 degrees. | The deflection gearing constant was 50.69 with 1 knot equal to 3.05 arc minutes, corresponding to 2275 fps at 2000 yards. Drift was corrected by inclining the sight 2 degrees. | ||
| Line 188: | Line 220: | ||
Sight lines were 10 inches above the bore, and 16 inches left and 15 inches right. Open sights and temperature correctors were provided. | Sight lines were 10 inches above the bore, and 16 inches left and 15 inches right. Open sights and temperature correctors were provided. | ||
The addition of depth charges obligated some ships to land their aft 4-in gun. | The addition of depth charges obligated some ships to land their aft 4-in gun.{{UKTHVol4Part34|p. 14}} | ||
Percussion firing gear to be fitted as soon as conveniently possible in dockyard was ordered for these guns in April, 1914.{{AWO1914|1045 of 24 Apr, 1914}} | |||
===12-pdr Guns=== | ===12-pdr Guns=== | ||
The two 12-pdr guns were mounted on the port and starboard beams. | The two 12-pdr guns were mounted on the port and starboard beams.{{TheSightM|pp. 4, 96, 108, Plate 46}} | ||
They were 12-pdr 12 cwt Q.F. guns on P V mountings with 100 rounds per gun, the same weapon as since the "Tribal" group.{{March|p. 109}} The mountings could elevate to 20 degrees and depress to 10. | They were 12-pdr 12 cwt Q.F. guns on P. V mountings with 100 rounds per gun, the same weapon as since the "Tribal" group.{{March|p. 109}} The mountings could elevate to 20 degrees and depress to 10. | ||
The sights were the only cam-worked 12-pdr sights in the Royal Navy, with range dials for 2150 fps, 1-in and .303-in aiming rifles. They could elevate to 20 degrees but their graduations ended at 19.25 degrees (8100 yards full charge). MV was corrected by adjustable pointer, +/- 100 fps. | The sights were the only cam-worked 12-pdr sights in the Royal Navy, with range dials for 2150 fps, 1-in and .303-in aiming rifles. They could elevate to 20 degrees but their graduations ended at 19.25 degrees (8100 yards full charge). MV was corrected by adjustable pointer, +/- 100 fps. | ||
Deflection gearing constant was 43.76, with 1 knot equalling 3.76 arc minutes, corresponding to | Deflection gearing constant was 43.76, with 1 knot equalling 3.76 arc minutes, corresponding to a muzzle velocity of 2197 fps at 2000 yards. | ||
Drift was corrected by inclining the sight 2 degrees. Sighting lines on the left were 10.25 inches above the bore and 10 inches left. The trainer's sighting lines were 12.25 inches above the bore and 10 inches right. His sight could be used as a [[Free Trainer's Sight|free sight]]. Open sights were provided (for the layer at least), but there is no sign of temperature correctors. | Drift was corrected by inclining the sight 2 degrees. Sighting lines on the left were 10.25 inches above the bore and 10 inches left. The trainer's sighting lines were 12.25 inches above the bore and 10 inches right. His sight could be used as a [[Free Trainer's Sight|free sight]]. Open sights were provided (for the layer at least), but there is no sign of temperature correctors. | ||
In late 1913, the P. Mark V and VI gun mountings had percussion firing gear ordered for them.{{AWO1913|718 of 12 Dec, 1913}} | |||
===Torpedoes=== | ===Torpedoes=== | ||
| Line 207: | Line 243: | ||
In July 1912, {{UK-Alarm}} had an explosive sweep fitted with an electrically-fired charge. In May 1918, {{UK-Nymphe}} had sweep gear, two depth charge throwers and 4 stern chutes with 12 charges. In August, 1918, {{UK-Brisk}} had two depth charge throwers, eight carriers, one runner and 23 charges. Paravane equipment was landed to compensate for this 7.5 tons of added weight.<ref>March.</ref> | In July 1912, {{UK-Alarm}} had an explosive sweep fitted with an electrically-fired charge. In May 1918, {{UK-Nymphe}} had sweep gear, two depth charge throwers and 4 stern chutes with 12 charges. In August, 1918, {{UK-Brisk}} had two depth charge throwers, eight carriers, one runner and 23 charges. Paravane equipment was landed to compensate for this 7.5 tons of added weight.<ref>March.</ref> | ||
Depth charges were added during the war to many of the ships, requiring some to surrender their aft 4-in gun. | Depth charges were added during the war to many of the ships, requiring some to surrender their aft 4-in gun.{{UKTHVol4Part34|p. 14}} | ||
==Fire Control== | ==Fire Control== | ||
| Line 213: | Line 249: | ||
===Instruments=== | ===Instruments=== | ||
By 1920, the ships in ''Acorn'' to ''Laforey'' classes had [[Wise Pressure Telegraphy System]]s in place to support fire control. | By 1920, the ships in ''Acorn'' to ''Laforey'' classes had [[Wise Pressure Telegraphy System]]s in place to support fire control.{{UKTH34|pp. 15-16}} | ||
===Rangefinders=== | ===Rangefinders=== | ||
A 1-m base rangefinder was supplied to all destroyers of the "Tribal" class through "L" class around 1916, but this was later withdrawn.{{UKTH23|pp. 31, 32}} | |||
== | ==Torpedo Control== | ||
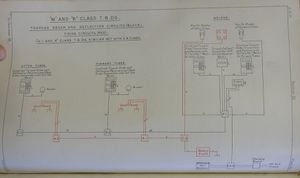
[[File:ARTS1917Plate84.jpg|thumb|300px|'''Electrical Instruments'''{{ARTS1917|Plate 84}}<br>found in most or all "Acorn" class destroyers]] | |||
The ships had a single sighting position located high up in the centre of the bridge, which required them to thus have only a single set of firing pushes or keys as well as keys for operating a buzzer at the forward torpedo mount and a rattler at the aft mount.{{ARTS1917|p. 211}} | |||
The data instruments used were electrical. A single Mark I deflection transmitter at the control position, and separate order transmitters and keys, one for the forward tubes and one for the aft. Each torpedo mount had a combined receiver for these signals.{{ARTS1917|p. 211, Plate 84. (C.I.O. 439/17.)}} | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 262: | Line 292: | ||
name=Acorn | name=Acorn | ||
pend=H.02 (1914)<br>H.03 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.02 (1914)<br>H.03 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[John Brown]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[John Brown & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
launch=1 7 1910{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | launch=1 7 1910{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
| Line 272: | Line 302: | ||
name=Alarm | name=Alarm | ||
pend=H.05 (1914)<br>H.04 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.05 (1914)<br>H.04 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[John Brown]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[John Brown & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
launch=29 8 1910{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | launch=29 8 1910{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
| Line 283: | Line 313: | ||
name=Brisk | name=Brisk | ||
pend=H.11 (1914)<br>H.70 (Sep 1915)<br>H.22 (Jan-Sep 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.11 (1914)<br>H.70 (Sep 1915)<br>H.22 (Jan-Sep 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[John Brown]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[John Brown & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
launch=20 9 1910{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | launch=20 9 1910{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
| Line 293: | Line 323: | ||
name=Sheldrake | name=Sheldrake | ||
pend=H.88 (1914)<br>H.0A (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.88 (1914)<br>H.0A (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Denny]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[William Denny & Brothers]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 305: | Line 335: | ||
name=Staunch | name=Staunch | ||
pend=H.89 (1914)<br>H.2A (1917){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.89 (1914)<br>H.2A (1917){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Denny]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[William Denny & Brothers]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
launch=29 10 1910{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | launch=29 10 1910{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
| Line 316: | Line 346: | ||
name=Cameleon | name=Cameleon | ||
pend=H.21 (1914)<br>H.24 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.21 (1914)<br>H.24 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Fairfield]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 326: | Line 356: | ||
name=Comet | name=Comet | ||
pend=H.25 (1914-1916){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.25 (1914-1916){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Fairfield]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 338: | Line 368: | ||
name=Goldfinch | name=Goldfinch | ||
pend=H.44 (1914){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.44 (1914){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Fairfield]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 351: | Line 381: | ||
name=Nemesis | name=Nemesis | ||
pend=H.72 (1914)<br>H.88 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.72 (1914)<br>H.88 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Hawthorn Leslie]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[Hawthorn Leslie & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 364: | Line 394: | ||
name=Nereide | name=Nereide | ||
pend=H.74 (1914)<br>H.89 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.74 (1914)<br>H.89 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Hawthorn Leslie]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[Hawthorn Leslie & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 375: | Line 405: | ||
name=Nymphe | name=Nymphe | ||
pend=H.83 (1914)<br>D.25 (Jan-Jun 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.83 (1914)<br>D.25 (Jan-Jun 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Hawthorn Leslie]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[Hawthorn Leslie & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 386: | Line 416: | ||
name=Fury | name=Fury | ||
pend=H.42 (1914)<br>H.35 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.42 (1914)<br>H.35 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Inglis]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[A. & J. Inglis]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 408: | Line 438: | ||
name=Larne | name=Larne | ||
pend=H.57 (1914)<br>H.50 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.57 (1914)<br>H.50 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Thornycroft]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[John I. Thornycroft & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 419: | Line 449: | ||
name=Lyra | name=Lyra | ||
pend=H.60 (1914)<br>H.67 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.60 (1914)<br>H.67 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Thornycroft]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[John I. Thornycroft & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 430: | Line 460: | ||
name=Martin | name=Martin | ||
pend=H.65 (1914)<br>H.71 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.65 (1914)<br>H.71 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Thornycroft]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[John I. Thornycroft & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 441: | Line 471: | ||
name=Minstrel | name=Minstrel | ||
pend=H.69 (1914)<br>H.82 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.69 (1914)<br>H.82 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[Thornycroft]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | builder=[[John I. Thornycroft & Company]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 454: | Line 484: | ||
name=Redpole | name=Redpole | ||
pend=H.77 (1914)<br>H.96 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.77 (1914)<br>H.96 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[J. | builder=[[J. Samuel White]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 465: | Line 495: | ||
name=Rifleman | name=Rifleman | ||
pend=H.82 (1914)<br>H.97 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.82 (1914)<br>H.97 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[J. | builder=[[J. Samuel White]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 476: | Line 506: | ||
name=Ruby | name=Ruby | ||
pend=H.85 (1914)<br>H.98 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | pend=H.85 (1914)<br>H.98 (Jan-Apr 1918){{DittColl|p. 61}} | ||
builder=[[J. | builder=[[J. Samuel White]]{{Conways1906|p. 74}} | ||
order= | order= | ||
laid= | laid= | ||
| Line 487: | Line 517: | ||
data --> | data --> | ||
[[Category:Featured Ship Classes]] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:31, 6 April 2022
Twenty destroyers of the Acorn Class were completed between 1910 and 1912.
They were re-designated as "H" class destroyers in October, 1913.[1]
From 1912-1916, they were serving in the Second and Fifth Destroyer Flotillas.[2][3]
They were the last British destroyers to feature a hand steering position.[4]
| Overview of 20 vessels | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citations for this data available on individual ship pages unless otherwise stated | ||||||
| Name | Builder | Laid Down | Launched | Completed | Fate | Cost[5] |
| Acorn | John Brown & Company | 1 Jul, 1910 | Nov, 1921 | £98,373 | ||
| Alarm | John Brown & Company | 29 Aug, 1910 | May, 1921 | £95,212 | ||
| Brisk | John Brown & Company | 20 Sep, 1910 | Nov, 1921 | £102,310 | ||
| Sheldrake | William Denny & Brothers | 18 Jan, 1911 | Nov, 1921 | £95,881 | ||
| Staunch | William Denny & Brothers | 29 Oct, 1910 | Torpedoed 11 Nov, 1917 | £93,053 | ||
| Cameleon | Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company | 1 Jun, 1910 | Nov, 1921 | £98,671 | ||
| Comet | Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company | 23 Jun, 1910 | Torpedoed 6 Aug, 1918 | £95,581 | ||
| Goldfinch | Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company | 12 Jul, 1910 | Wrecked 19 Feb, 1915 | £94,758 | ||
| Nemesis | Hawthorn Leslie & Company | 9 Aug, 1910 | To Japan Jun, 1917 | £97,752 | ||
| Nereide | Hawthorn Leslie & Company | 6 Sep, 1910 | Dec, 1921 | £95,673 | ||
| Nymphe | Hawthorn Leslie & Company | 31 Jan, 1911 | May, 1921 | £94,895 | ||
| Fury | A. & J. Inglis | 25 Apr, 1911 | Nov, 1921 | £95,793 | ||
| Hope | Swan Hunter | 6 Sep, 1910 | Feb, 1920 | £94,574 | ||
| Larne | John I. Thornycroft & Company | 23 Aug, 1910 | May, 1921 | £89,838 | ||
| Lyra | John I. Thornycroft & Company | 4 Oct, 1910 | May, 1921 | £86,267 | ||
| Martin | John I. Thornycroft & Company | 15 Dec, 1910 | Aug, 1920 | £85,243 | ||
| Minstrel | John I. Thornycroft & Company | 2 Feb, 1911 | To Japan Jun, 1917 | £85,141 | ||
| Redpole | J. Samuel White | 24 Jun, 1910 | May, 1921 | £97,081 | ||
| Rifleman | J. Samuel White | 22 Aug, 1910 | May, 1921 | £94,866 | ||
| Ruby | J. Samuel White | 4 Nov, 1910 | May, 1921 | £94,617 | ||
Fittings
Minstrel and Nereide had experimental water-excluding ventilators, and were asked to report on their effectiveness just as the war was about to start.[6]
In October 1914, as the Acorns were all serving in the Second Destroyer Flotilla, they were ordered to have the (hydraulic?) searchlight control system first used in H.M.S. Badger fitted.[7]
Performance
Six of the ships were found to have developed leaks caused by vibration at high speed running: Acorn, Alarm, Larne, Lyra, Nymphe and Rifleman.[8]
They burned oil, unlike the Beagles, delivering the same 27 knots on a displacement 200 tons lighter.[9]
While the individual ships certainly varied widely, they were described as having a radius of 2250 NM at 13 knots.[10]
Acorn achieved 4 miles to the ton of coal at 27.5 knots. Redpole topped out at a spry 30.61 knots in rough weather![11]
Comet had the smallest tactical diameter (402 yards starboard, 536 port, advance of 354 yards), and Redpole had the worst diameters at 728 yards to starboard and 608 to port. The ships burned around 7 tons per hour at full speed and 0.75 tons per hour at cruising speed.[12]
In foul weather, the commander of Goldfinch commented, "I cannot say anything bad enough for the chart house, all charts ruined and a foot of water on deck, even battened down with all deadlights screwed down hard the water poured in, even through the keyhole..." but praised the ship as "simply perfect to handle and turns wonderfully considering her length." In especially severe seas, the Beagles came through fine, but the Acorns suffered from what was blamed as faulty riveting. The ships would often pitch up out of the sea as far back as their bridge and would slam down hard, knocking men from their feet in the stokeholds and bridge.[13]
Jellicoe was annoyed by the meager radius of action for the class: 766 miles at 25 knots. Here, as well there was considerable variation: from 630 miles for Nereide to 925 miles for Cameleon.[14]
Armament
The gun armament used here was similar to that of the preceding Beagle class, although the 12-pdrs were no longer mounted in echelon. A similar scheme would carry forward into the Acheron class with minor variations in mountings and positioning of the 12-pdrs.
In late September, 1914, the Admiralty ordered that the guns on the Tribals and later classes were to be given loading lights, initially on temporary circuits.[15]
4-in Guns
The two 4-in guns mounted fore and aft were 4-in B.L. Mark VIII on P. III mountings with 120 rounds per gun.[16][17]
The mounting could elevate to 20 degrees and depress to 10 degrees, but though its sight could match the 20 degree elevation, the range dial was only graduated to 9,300 yards (14 degrees 44 arc minutes) at 2,225 fps.
The gear-worked sight had a range gearing contant of 54 and spiral-reading range dials were provided for 2225 fps, 1-in aiming rifle and .303-in aiming rifle. M.V. could be corrected by adjustable pointer to +/- 75 fps.
The deflection gearing constant was 50.69 with 1 knot equal to 3.05 arc minutes, corresponding to 2275 fps at 2000 yards. Drift was corrected by inclining the sight 2 degrees.
Sight lines were 10 inches above the bore, and 16 inches left and 15 inches right. Open sights and temperature correctors were provided.
The addition of depth charges obligated some ships to land their aft 4-in gun.[18]
Percussion firing gear to be fitted as soon as conveniently possible in dockyard was ordered for these guns in April, 1914.[19]
12-pdr Guns
The two 12-pdr guns were mounted on the port and starboard beams.[20]
They were 12-pdr 12 cwt Q.F. guns on P. V mountings with 100 rounds per gun, the same weapon as since the "Tribal" group.[21] The mountings could elevate to 20 degrees and depress to 10.
The sights were the only cam-worked 12-pdr sights in the Royal Navy, with range dials for 2150 fps, 1-in and .303-in aiming rifles. They could elevate to 20 degrees but their graduations ended at 19.25 degrees (8100 yards full charge). MV was corrected by adjustable pointer, +/- 100 fps.
Deflection gearing constant was 43.76, with 1 knot equalling 3.76 arc minutes, corresponding to a muzzle velocity of 2197 fps at 2000 yards.
Drift was corrected by inclining the sight 2 degrees. Sighting lines on the left were 10.25 inches above the bore and 10 inches left. The trainer's sighting lines were 12.25 inches above the bore and 10 inches right. His sight could be used as a free sight. Open sights were provided (for the layer at least), but there is no sign of temperature correctors.
In late 1913, the P. Mark V and VI gun mountings had percussion firing gear ordered for them.[22]
Torpedoes
Two single 21-in tubes on the centre line, firing the Mark II torpedo.[23]
Other Weapons
In July 1912, Alarm had an explosive sweep fitted with an electrically-fired charge. In May 1918, Nymphe had sweep gear, two depth charge throwers and 4 stern chutes with 12 charges. In August, 1918, Brisk had two depth charge throwers, eight carriers, one runner and 23 charges. Paravane equipment was landed to compensate for this 7.5 tons of added weight.[24]
Depth charges were added during the war to many of the ships, requiring some to surrender their aft 4-in gun.[25]
Fire Control
By 1915, at least, these ships also had fixed voice pipes installed between decks with the last lengths being flexible (one voice pipe for gunnery, one for torpedoes) fitted between bridge and guns, torpedo tubes, and searchlights. A third voicepipe, entirely flexible, ran from bridge to the forward gun.[26]
Instruments
By 1920, the ships in Acorn to Laforey classes had Wise Pressure Telegraphy Systems in place to support fire control.[27]
Rangefinders
A 1-m base rangefinder was supplied to all destroyers of the "Tribal" class through "L" class around 1916, but this was later withdrawn.[28]
Torpedo Control
The ships had a single sighting position located high up in the centre of the bridge, which required them to thus have only a single set of firing pushes or keys as well as keys for operating a buzzer at the forward torpedo mount and a rattler at the aft mount.[30]
The data instruments used were electrical. A single Mark I deflection transmitter at the control position, and separate order transmitters and keys, one for the forward tubes and one for the aft. Each torpedo mount had a combined receiver for these signals.[31]
See Also
Footnotes
- ↑ Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. p. 74.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916. p. 87.
- ↑ Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. p. 74.
- ↑ March. British Destroyers. pp. 115.
- ↑ Navy (Dockyard Expense Accounts), 1912–1913. p. 143.
- ↑ Admiralty Weekly Order No. 184 of 24 July, 1914.
- ↑ Admiralty Weekly Order No. 454 of 6 Oct, 1914.
- ↑ "Good Firing On The China Station." The Times (London, England), Saturday, Jul 08, 1911; pg. 15; Issue 39632.
- ↑ The Technical History and Index, Vol. 4, Part 34. p. 11.
- ↑ March. British Destroyers. p. 109.
- ↑ March. British Destroyers. p. 113.
- ↑ March. British Destroyers. p. 113.
- ↑ March. British Destroyers. pp. 113-114.
- ↑ March. British Destroyers. p. 115.
- ↑ Admiralty Weekly Order No. 416 of 29 Sep, 1914.
- ↑ March. British Destroyers. p. 109.
- ↑ The Sight Manual. 1916. pp. 4, 88, 108, Plate 42.
- ↑ The Technical History and Index, Vol. 4, Part 34. p. 14.
- ↑ Admiralty Weekly Order No. 1045 of 24 Apr, 1914.
- ↑ The Sight Manual. 1916. pp. 4, 96, 108, Plate 46.
- ↑ March. British Destroyers. p. 109.
- ↑ Admiralty Weekly Order No. 718 of 12 Dec, 1913.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1909. p. 32.
- ↑ March.
- ↑ The Technical History and Index, Vol. 4, Part 34. p. 14.
- ↑ Manual of Gunnery, Vol. III., 1915., p. 150.
- ↑ The Technical History and Index, Vol. 4, Part 34. pp. 15-16.
- ↑ The Technical History and Index, Vol. 3, Part 23. pp. 31, 32.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1917. Plate 84.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1917. p. 211.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1917. p. 211, Plate 84. (C.I.O. 439/17.).
Bibliography
- Gray, Randal (editor) (1985). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. London: Conway Maritime Press. (on Amazon.com and Amazon.co.uk).
- March, Edgar J. (1966). British Destroyers: A History of Development, 1892-1953. London: Seeley Service & Co. Limited. (on Bookfinder.com).
- Admiralty, Technical History Section (1920). The Technical History and Index: Alteration in Armaments of H.M. Ships during the War. Vol. 4, Part 34. C.B. 1515 (34) now O.U. 6171/20. At The National Archives, Kew, United Kingdom.
| Acorn Class Destroyer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acorn | Alarm | Brisk | Sheldrake | Staunch | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cameleon | Comet | Goldfinch | Nemesis | Nereide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nymphe | Fury | Hope | Larne | Lyra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Martin | Minstrel | Redpole | Rifleman | Ruby | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <– | Beagle Class | Destroyers (UK) | Acheron Class | –> | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||